For archaeologists, proving that Prehistoric art was made in a certain year was a big problem right away.
Even now, it can be hard for scholars to agree on a date for the art.
Carbon dating has been the biggest help to the process since the 1990s, when it was used a lot more.
Because some cave art materials, like charcoal and beeswax, contain organic carbon that can be reliably dated, carbon dating is now the most common way to get an exact date on cave art.
Archaeologists use a technique known as “dating” to determine the age of objects. As an example, if you find a piece of art in a cave, the closer to the surface it is, the older it is. Two new approaches to studying cave art were devised by the first researchers. One was based on assumptions from archaeology, and the other was based on historical art techniques. On the other hand, they compared the artwork they found in the cave to ancient artefacts they had previously discovered.
The researchers used a method known as “parietal stratigraphy.” It was believed that the figures at the bottom of a composition were more ancient than those at the top if they were in two or more distinct styles. Art history students typically employ both of these strategies. Other means of dating cave art were unavailable until around 25 years ago. In spite of modern dating procedures, we were still unable to date the cave art we were studying. The initial framework was built on a foundation of stylistic analysis.
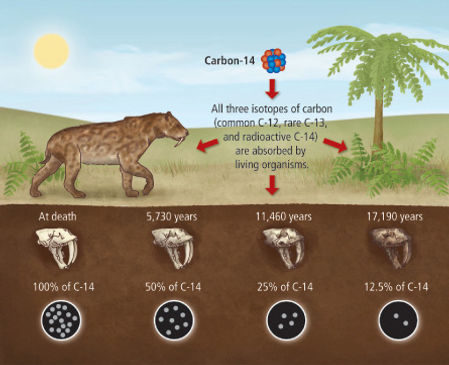
By the early 1990s, radiocarbon dating methods had advanced to the point where they could be used on small amounts of material. Biological materials such as trees, animals, and humans contain Carbon-14, an unstable radioactive isotope.
These materials can be radiocarbon dated based on the amount of C14 they contain. As soon as the organism ceases to exist, it begins to decompose at a steady rate, but it never stops. Because C14 is radioactive, it can tell us when an organism died. As a result, charcoal drawings made with tree branches could be used to date things in prehistoric cave art.
Only a quarter of the images used charcoal, while a third made use of black pigments. This approach isn’t perfect, but it’s better than nothing. Because the method was so new, the results had to be taken with a grain of salt. It was possible to make progress, but we had to be careful and use scientific reasoning when analysing the dates.
In the last decade, new methods for determining the age of cave art have emerged. Using uranium series dating, for example, one can ascertain the age of an artwork. It works in the same way as Radiocarbon because it is based on another radioactive isotope. Calcite dating cannot be done using this technique. There are two ways that calcification occurs in caves and on walls, where it can grow over carved designs.
The benefits of a new approach are undeniable, but so are the drawbacks. A wonderful opportunity for further study! For the most part, scientists worked in the same way they had since the turn of the 20th century, until these new approaches appeared. There was a lot of debate following the publication of the updated results.
In France, it’s known as Chauvet cave and dates back to 1994 when it was first discovered. The cave art in Western Europe is among the most complex and detailed in the world. Around 15,000 years ago, this is thought to be the final stage of the Upper Palaeolithic.
Many people were surprised by the results of dating the figures, bones, and charcoal found on the floor. One of the earliest forms of art produced by modern humans, when it was first created. In spite of these issues, there is a fierce debate that continues to this day.
C14 and U-Series dating requires the cooperation of archaeologists, geologists, and chemists. Preliminary research into cave art’s origins has found that both methods have been extremely useful. Even though we’ve made some progress, we still have a long way to go before we’re ready for prime time.
When it comes to art that wasn’t made with charcoal, we can’t completely rely on the methods. Although we can date cave art using science, we must still rely on methods like stylistic comparisons to determine how old things are.
