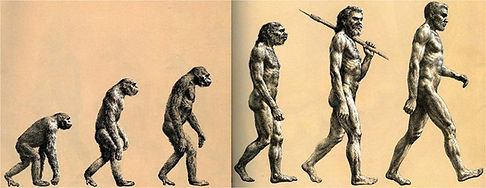
The very beginning of artifactual history dates back to more than 2 million years ago, in east-central Africa (the most accepted area for the origin of the first humans).
It was here that Homo habilis (also known as ‘handy man’), enabled the use of manual processes where they were able to use pebbles to create tools, they did this by cutting off a piece of the surface so that they could work with it, and form it into one of the earliest forms of rudimentary tools.

Homo habilis
One million years later, Homo erectus innovated a much more effective tool in which they discovered they could chip away the face of an opposite stone to give it a sharp edge.
A quarter of a million years later, we have found evidence that humans were making tools that could be used for many different things such as a hand axe. We also found that they shaped and smoothed stones into a shape that was more or less the same all over. This shows that they were aware of how things looked and how they worked together. (This is the first example of the awareness of form and shape within humans, hence allowing the ability to observe and create to be strengthened within our brains).

Homo erectus
Moving to 125,000 years ago, Neanderthal man (Homo sapiens neanderthalensis) who roamed around in Europe & western Asia have been found to have coloured their bodies in red ochre. Although we do not fully understand the reasoning the behind this, it is safe to say that that this sub-species had a thought of life extending beyond our physical world, with graved being dug for the dead, and being buried with weapons, tools, and gifts including food (this was discovered in La Ferrassie (France)). We discovered a monument that was based around this period of time, in which a large stone had had cup like marking being pecked out of it. It is thought that these markings had a commemorative meaning to them, and so would prove the next stage towards the evolution of art, and creating.

Neanderthal man
Neanderthal man vanished with the last Ice Age in 40,000 BC, leaving Homo sapiens as the only human species to survive the Ice Age. They had carved out the earliest known objects into what we now call ‘art’ before the end of the Ice Age.
Unfortunately, the stone carvings that have survived from this period cannot be accurately dated, and thus cannot be fully claimed to be the ‘earliest known works of art,’ because the only piece that can be dated is from 5,000 years ago, and thus falls under the category of ‘history,’ rather than ‘prehistory.’ These sculptures have been discovered across a large area of Europe and Russia, and they are far more rare than tools or weapons from this time period.